Overview
A recent study by the Goa Institute of Management (GIM) and the Cochin University of Science and Technology (CUSAT) has shed important light on how consumers react emotionally to AI-enabled service agents like chatbots, digital assistants, and service robots. The research shows how the appropriate degree of humanisation in chatbots can greatly increase customer comfort and trust as AI becomes a common channel for customer service interactions across industries.
AI’s Expanding Use in Regular Service Interactions
AI is frequently used by modern consumers in banking, retail, healthcare, hospitality, travel, and customer service. Understanding how AI behaviour affects emotional comfort, acceptance, and satisfaction becomes crucial as companies automate customer touchpoints.
The study, which was published in the International Journal of Consumer Studies, examined how consumers feel, think, and act during AI-driven service interactions by analysing insights from 157 peer-reviewed papers published in 44 prestigious journals.
Crucial Realisation: Humanisation Balance Builds Trust
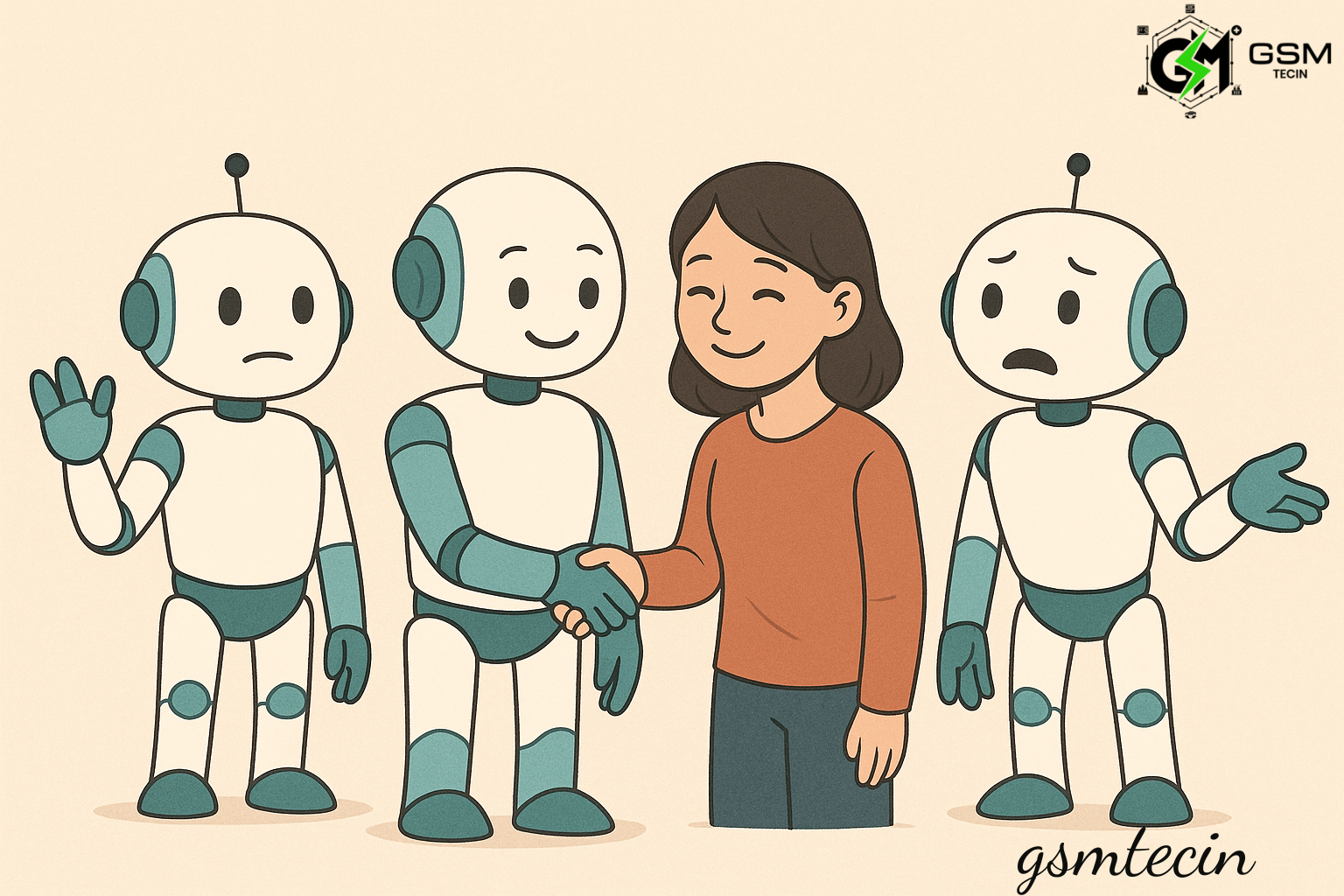
The study comes to the conclusion that when chatbots have a balanced degree of human-like characteristics, they have the most beneficial effects. Consumers react favourably when AI exhibits:
- Kindness and warmth
- A sympathetic and encouraging tone
- Conversational, organic language
- Being courteous and sensitive to emotions
These attributes improve comfort, foster long-term client engagement, and increase trust.
The study cautions that too much human resemblance in chatbot design can be uncomfortable. Exaggerated friendliness, excessively expressive emotions, or attempts to fully mimic human identity may make users feel duped or controlled, which will ultimately erode trust.
Why Consumers React to AI Emotionally
Even when social cues are given by machines, people respond to them unconsciously. Simple expressions of empathy, such as “I know how frustrating that must feel,” can:
- Cut down on stress
- Boost adoption of automated assistance
- Boost customer patience and cooperation
- Boost the perception of the calibre of services
On the other hand, excessively human behaviour can lead to scepticism, and robotic language can come across as cold and contemptuous. The most reliable chatbots balance emotional sensitivity with efficiency.
Integrated Framework for AI Behaviour and Customer Outcomes
The study introduces a comprehensive framework showing that customer reactions depend on the combined influence of:
| Component | Impact |
|---|---|
| AI Design Features | Empathy, tone, reliability, interaction style |
| Customer Traits | Personality, cultural background, experience with tech |
| Service Context | Industry sensitivity, urgency of the interaction |
Customers are more satisfied, less irritated, and more inclined to interact with automated channels again when these factors are in harmony.
Industry-Wide Impact of Balanced Humanised AI
The benefits of emotionally intelligent chatbots span across sectors:
| Industry | Result |
|---|---|
| Banking | Increases trust in financial transactions |
| Healthcare | Offers calm guidance and emotional reassurance |
| Retail | Creates personalised shopping support |
| Travel & Hospitality | Helps reduce stress during disruptions |
| Education | Supports comfortable and interactive digital learning |
Businesses adopting balanced AI humanisation see improved retention, satisfaction, and long-term engagement.
Chatbot Design: Ethics and Cultural Sensitivity
The study highlights that a fundamental tenet of chatbot design is ethical transparency. Customers should never be deceived or emotionally coerced by excessively human-like interaction, and users should always be conscious that they are interacting with AI.
Responsible AI humanisation includes:
- Disclosure of chatbot identity
- Careful, non-manipulative use of emotional language
- Protection of user privacy and data
The study also highlights research gaps such as cultural differences in AI perception, social identity effects, and evolving attitudes toward emotional AI.
Future of Chatbot Experience: Emotionally Smart, Not Fully Human
While developments in sentiment analysis and natural language processing are quickly expanding the capabilities of chatbots, research indicates that good chatbot design does not aim to replace human identity but rather to provide users with empathy while being open about being artificial intelligence. Technology that acknowledges human emotions while solving problems is preferred by consumers over technology that attempts to imitate human behaviour.
In conclusion
The GIM-CUSAT study makes one thing clear: customer comfort depends on balance. Chatbots that interact with people in a natural, compassionate, and kind manner without feigning humanity have the highest levels of trust and satisfaction. Effective chatbot design that is both transparent and emotionally intelligent will be essential to creating enduring and significant customer relationships as AI continues to influence digital service channels.