SpaceX Gets Ready for Sunday’s Launch of the Starship Megarocket
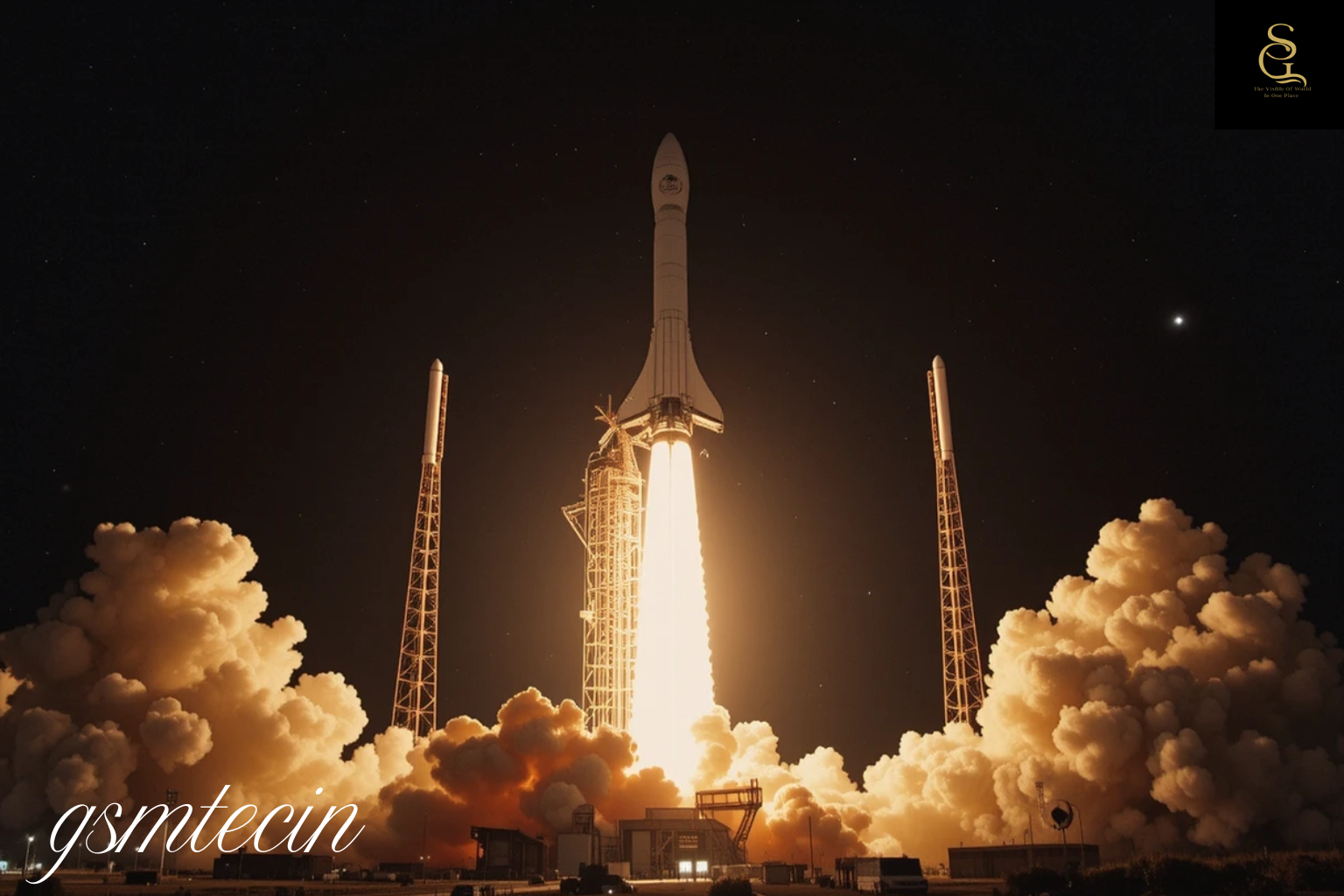
This Sunday, Elon Musk’s private space exploration firm SpaceX will launch its Starship megarocket. The launch marks a significant milestone in SpaceX’s ambitious plans for interplanetary travel, including missions to the Moon and Mars. With its unparalleled size, payload capability, and fully reusable design, Starship promises to transform spaceflight and make space travel more affordable and environmentally friendly.
Can You Explain Starship?
The two primary parts of Starship, a next-generation spacecraft, are:
Super Heavy Booster: The thrust to escape Earth’s gravity is provided by this first stage, which is about 230 feet tall. It is the strongest rocket stage ever constructed, with up to 33 Raptor engines.
The 160-foot-tall Starship spacecraft sits atop the booster and will transport people and cargo into orbit, the Moon, or Mars.
With a combined length of over 390 feet, the system surpasses NASA’s Saturn V as the largest rocket ever built. SpaceX’s goal to increase access to space and reduce launch costs is largely dependent on its reusability.
Why This Launch Is Happening
The purpose of Sunday’s flight is to test Starship in actual flight conditions. High-altitude flights and brief hops were part of earlier tests. This launch will evaluate:
The separation of boosters
Performance of the engine during ascent
Durability of the heat shield during reentry
controlled landing for possible repurposing
The mission is essential for confirming Starship’s design and preparedness for upcoming crewed or cargo flights, even though there are no astronauts on board. Engineers will analyze the data from this flight and implement improvements to ensure Starship performs reliably on more ambitious missions.
Launch Time and Site Details
At SpaceX’s Starbase facility in Boca Chica, Texas, the launch is planned for 6:30 p.m. local time (2330 GMT/5:00 a.m. IST). The weather and pre-launch inspections determine the precise time. The site has become a gathering place for aerospace enthusiasts and has seen several Starship prototype tests.
Methods for Observation
Engineer and mission control commentary is available on SpaceX’s YouTube live streaming service. SpaceX also posts updates on social media. Although authorities designate approved viewing spots near Boca Chica, they advise spectators to keep a safe distance. The Super Heavy booster produces over 16 million pounds of thrust, creating a loud sonic boom and a massive flame plume.
Impact of Starships
Starship is an example of a revolutionary development in aerospace technology:
Launch expenses could be significantly reduced by a fully reusable design.
In line with Musk’s interplanetary vision, Mars colonisation is intended to deliver people and goods to the planet.
Moon Missions: For the Artemis program, NASA intends to use a modified Starship as a lunar lander.
Extension of the Space Economy: Its payload capability (up to 100 metric tonnes to low Earth orbit) facilitates infrastructure projects, asteroid mining, satellite deployment, and space tourism.
Earlier Starship Examinations
From high-altitude flights to low-altitude hops, Starship has undergone a number of well-publicized tests:
The first high-altitude flight was SN8 (Dec. 2020); it descended successfully but landed explosively.
SN10 (March 2021): A soft landing was accomplished, followed by an explosion a few minutes later.
In May 2021, SpaceX achieved an important milestone with the successful high-altitude flight and landing of SN15.
Through iterative testing, SpaceX is able to learn from mistakes and improve the design of Starship.
Environmental and Safety Concerns
There are risks associated with launching a rocket the size of Starship. The FAA and SpaceX collaborate to guarantee adherence to environmental and safety standards. Launch windows are communicated to the people of Boca Chica. In addition, SpaceX is looking into ways to lessen its impact on the environment, such as cutting emissions and preserving local wildlife.
Obstacles to Come
Despite advancements, there are still technical difficulties:
Enhancing the separation of boosters
Maintaining the integrity of the heat shield during reentry
Reaching complete and quick reusability
Overseeing the integration of payloads for various missions
Every test yields information that advances Starship’s operational preparedness.
Recent Failures
During three Starship test flights in 2025—over Caribbean islands or during ground tests—upper-stage explosions ended the missions. Engineers attributed the structural flaws to efforts to lighten the vehicle to carry heavier loads. SpaceX’s “fail fast, learn fast” strategy still directs development in spite of these setbacks.
Analysts point out that SpaceX is undr a lot of pressure to prove dependability because recent setbacks have eclipsed earlier achievements. Key challenges still include sustaining low-cost reusability and achieving super-cooled propellant refuelling in orbit.
The Prospects for Starship
Should it be successful, Starship could help:
Deployment of commercial satellites
NASA Moon missions for Artemis
Possible colonisation and exploration of Mars
Space travel
Spaceflight might become as commonplace as air travel due to its reusability, creating new opportunities for both commercial and scientific endeavours.
In conclusion
An important turning point in SpaceX’s roadmap is the impending launch of Starship. It could revolutionise human space exploration due to its size, reusability, and interplanetary objectives. The mission demonstrates SpaceX’s dedication to pushing the limits of aerospace engineering, regardless of whether it is a complete success or provides insights from setbacks.
SpaceX keeps proving that humanity can reach farther into the cosmos than ever before with creativity, tenacity, and audacious vision.