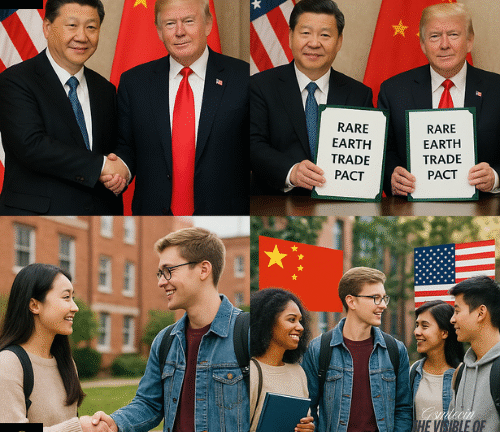
A significant change in trade, security, and diplomacy is marked by the Trump-China rare earths deal
Former US President Donald Trump made headlines when he proposed a significant trade deal with China that might change U.S.-China ties and global supply networks. The agreement centres on China’s pledge to restart supplying the US with vital rare earth elements and industrial magnets, subject to final approval by Trump and Chinese President Xi Jinping. Advanced manufacturing, clean energy systems, and military technology all depend on these materials.
An Agreement Amid Increasing Tensions
Following months of increased trade tensions following Trump’s second inauguration in January 2025, the agreement was reached. In April, the United States slapped a new round of tariffs known as the “Liberation Day” duties, which imposed an extra 34% levy on Chinese imports, increasing the overall tariff burden to 54%. China retaliated by imposing further export restrictions on rare earth elements and similar taxes on American exports, pushing bilateral levies to 125% and seriously upsetting global supply networks.
Rare earths had become the main negotiating chip as the two sides’ talks had reached a standstill. China controls around 90% of the world’s capacity for refining rare earth elements, therefore its limits led to significant production delays in U.S. businesses, such as defence contractors and the automobile industry.
Trump said in his announcement, which was posted on Truth Social:
- “After final confirmation with President Xi and me, our agreement with China is complete. China will provide full magnets and any rare earths that are required in advance. The relationship is great!
As a beneficial outcome of the accord, he also mentioned that the United States will allow Chinese students to complete their education in American universities.
Important Elements of the Contract
China will resume and ensure upfront supply of vital rare earths, such as neodymium, samarium, and dysprosium, to the United States.
Reduced U.S. Tariffs: According to reports, China will only be subject to a 10% tariff rate on agreed-upon categories, while Trump declared a 55% overall tariff rate for the U.S. side.
Restoring Student Exchanges: Teachers and Chinese families applaud the agreement, which permits Chinese students to attend American colleges.
Access to Infrastructure Bidding: It has been claimed that Chinese businesses will be permitted to submit bids on clean energy and infrastructure projects in the United States, however this is still pending regulatory review.
Economic and Strategic Importance
In industries like semiconductors, electric cars, missile systems, and wind turbines, rare earth elements are essential. The United States has long been at risk from China’s near-monopoly on rare earths. This weakness was made clear by the nation’s export limitations for 2025, which caused big American corporations like Ford to temporarily halt operations.
This agreement is seen by analysts as a practical, if short-term, solution to a structural imbalance. In addition to stabilising an unstable situation, it emphasises how urgently the United States must diversify its sources and develop domestic rare earth processing.
Exchange of Education: A Diplomatic Victory
A key component of the agreement is educational exchange between the United States and China, which is frequently neglected in hardline political discourse. The annual economic contribution of Chinese students to the United States exceeds $14 billion. Restoring student visas could promote long-term goodwill and ease diplomatic tensions.
Furthermore, Xi Mingze, the daughter of Chinese President Xi Jinping, attended Harvard, demonstrating the personal resonance of educational diplomacy. Allowing students to travel freely promotes international integration and understanding between the two countries.
Support, scepticism, and strategic doubts were the responses
The Trump administration frames the agreement as advantageous for both national security and economic objectives, praising it as a powerful example of his negotiating skills. Proponents see it as an essential step to safeguard American interests without intensifying hostilities.
Critics wonder if it increases American reliance on a single source. Even with assurances, national security experts warn that relying too much on Chinese supply chains may present concerns in the future. The ecological and human impacts of China’s increased mining activities are another issue that worries environmentalists.
China, however, presents the deal as a “win-win” situation. Beijing’s responsible role in the world and its intention to preserve peaceful commercial relations in spite of ideological and geopolitical differences were highlighted by state media.
The More Comprehensive View
Although this deal is a tactical win for all parties, it doesn’t address more fundamental issues. Geopolitical specialists anticipate more conflict in the areas of ideology, technology, and the military. However, the agreement might provide both nations some breathing room to stabilise their economies and prevent an escalation.
To lessen reliance on China, other countries including Australia, Canada, and Japan are still working to establish alternate rare earth supply chains.
Investors, legislators, and strategic strategists will be intently watching the implications of this agreement as it develops. It remains to be seen whether it turns out to be a long-term fix or a temporary measure before a new stage of the trade dispute.